Summary
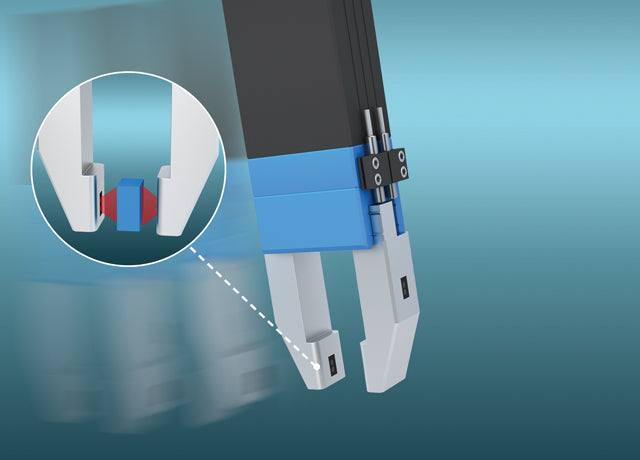
During automated production of electronic equipment, compact multi-finger robot grippers transport printed circuit boards and moldings between operations. During picking, process engineers require reliable confirmation that parts are correctly positioned in the gripper jaws. Miniature distance sensors, embedded in the gripping surfaces of the jaw fingers, sense the position of parts as the jaws close, avoiding positioning errors.
Customer Values
- Embedded miniature distance sensors ensure reliable detection of target positions, preventing damage to delicate PCBs and assemblies
- Compact 4mm x 4mm x 11mm sensor envelope with no external housing allows easy integration in tight spaces
- Sensing distances of up to 40mm offer designers highly versatile options when specifying equipment
- Industry-standard PNP analog output with a range of 0.3V to 3V allows scope for in-situ adjustment
- Proven technology ensures fit-and-forget operation with no manual intervention
- Non-contact solution maintains production throughput and minimizes cost of quality
- Cost-effective alternative to complex vision systems for applications with modest throughput rates of relatively high-value parts
Specific Product Advantages
- Miniature, housing-free photoelectric distance sensors suitable for easy integration
- 0.3V to 3V analog output with PNP interface and minimal power consumption
- Sensor weight only 3.1 grams with a compact 4mm x 4mm x 11m envelope
- Industry-standard -25°C to +65°C operating range
- Reliable, compact vibration-resistant sensors
Customer Application
Accuracy is everything during automated assembly and test of densely populated electronic equipment. Failure to align and present parts correctly at any stage results in costly and time-consuming rejects, often leading to assembly-line stoppages that require manual intervention. For manufacturers relying on fully automated, 24-hour operations, it’s an unwanted and expensive occurrence.
In an assembly-and-test cell, small surface-mounted printed circuit boards are inserted into molded plastic carriers before being presented for automated testing. At each stage, compact multi-finger robot grippers, which are programmed individually according to the geometry of both the parts and the production equipment, transport PCBs and assemblies between operations.
At any stage, small variations may occur in the positions of PCBs and assemblies as they are presented. When picking from matrix trays, commonly used for bulk transport, reliable confirmation is essential that each part is correctly positioned in the gripper jaws. A cost-effective alternative to complex vision systems is required for applications with modest throughput rates of relatively high-value parts.
Customer Solution
Production engineers specified grippers fitted with Contrinex MiniDist photoelectric sensors as a reliable and cost-effective means of confirming the position of PCBs in the jaws. When gripping PCBs and assemblies for transport to the next operation, these miniature distance sensors, embedded in the gripping surfaces of the jaw fingers, sense the position of each part as the jaws close.
MiniDist sensors are designed with the needs of OEMs and system integrators in mind and provide an unobtrusive fit-and-forget solution. These miniature devices weigh only 3.1 grams, and with a compact 4 x 4 x 11 mm envelope and no external housing, they allow easy integration in tight spaces with insufficient room for traditional devices.
With sensing distances of up to 40 mm, MiniDist devices offer designers highly versatile options when specifying equipment. An industry-standard PNP analog output ensures optimum flexibility, with an output range of 0.1V to 2.6V allowing scope for in-situ adjustment. Connection is via a 4-wire PVC-sheathed cable with a 2-meter standard length; alternative options are available on request.
These highly versatile miniature sensors meet the customer’s need for reliable operation while avoiding positioning errors. The solution is both highly flexible and cost-effective with minimal in-process rejects; production throughput is maintained at or above target levels while minimizing the cost of quality.